Every vehicle spends most of its life exposed to sunlight and fluctuating temperatures. Over time, these natural forces can slowly wear down paint, making it fade, crack, or lose its deep shine. That’s why modern car owners rely on paint protection film—a transparent barrier engineered to defend the vehicle’s surface from environmental stress.
At TintedAF, understanding how paint protection film reacts under extreme heat and prolonged sun exposure is essential. It’s not just about aesthetics—it’s about chemistry, durability, and how advanced materials protect your vehicle’s finish under the toughest conditions.
Understanding the Impact of Sun and Heat on Vehicle Surfaces
Heat and sunlight constantly challenge a car’s exterior. Prolonged exposure leads to paint oxidation, fading, and reduced gloss. While modern clear coats are designed for resilience, they’re not invincible against UV radiation and infrared heat that can penetrate deep into surface layers.
Why Studying Paint Protection Film Behavior Matters
Knowing how PPF performs under thermal and solar stress helps car owners appreciate why it’s more than just a film. It’s a living layer of polymer science that flexes, contracts, and adapts to maintain a stable barrier—no matter how high the temperature climbs.
What Paint Protection Film Is Made Of
Exploring the Layers: From Adhesive to Top Coat
A quality Paint Protection Film Dearborn is made of multiple layers. The adhesive base forms a bond with the paint, the middle thermoplastic layer absorbs impact, and the top coat resists scratches and UV degradation. Each layer contributes to how the film withstands prolonged exposure to sunlight and heat.
The Role of Thermoplastic Urethane (TPU) in Durability
TPU, the backbone of most films, is known for flexibility and strength. It expands when heated and returns to its original state when cooled. This elasticity allows the film to adapt without tearing or distorting, maintaining protection and appearance even in harsh sunlight.
How Heat Affects the Structure of Paint Protection Film
The Science of Thermal Expansion and Contraction
When a car sits in direct sunlight, its surface temperature can exceed 140°F. The film stretches microscopically to match this expansion. As temperatures cool, it contracts back to normal, a cycle known as thermal expansion and contraction. Repeated cycles can strain lesser-quality films but are easily managed by high-grade polymers.
What Happens at the Molecular Level During Heat Exposure
Under heat, molecular chains within the film become more active. This movement increases flexibility and helps prevent cracking. However, extreme heat over extended periods can weaken some molecular bonds, making it vital for films to contain stabilizers that limit degradation.
How Continuous Heat Influences Adhesion Over Time
Adhesives in paint protection film are pressure-sensitive. If they overheat, they may soften temporarily. Quality films are engineered to resist this effect, maintaining a consistent grip without bubbling, peeling, or slipping—crucial in sunny environments.

The Effects of Sunlight and Ultraviolet Radiation
How UV Rays Interact with the Film’s Chemical Bonds
UV radiation consists of high-energy photons that break down organic molecules. When these rays reach the film, they can disrupt carbon bonds unless stabilized. High-quality PPF includes UV-absorbing compounds that intercept this radiation before it can cause damage.
Understanding Oxidation and Photo-Degradation
Over time, UV exposure can trigger oxidation, where oxygen molecules interact with the film’s polymers, reducing transparency and elasticity. This process, known as photo-degradation, is one of the main reasons some films yellow or haze without proper UV protection additives.
Heat Resistance in High-Quality Paint Protection Film
The Function of UV Stabilizers and HALS Compounds
Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers (HALS) are molecular guardians that neutralize free radicals formed during UV exposure. They protect both the film and the paint beneath it from photochemical breakdown. Together with UV absorbers, they ensure the film stays clear and intact under constant sun exposure.
How Modern Films Manage Heat Dissipation
Advanced paint protection film products use micro-engineered polymers that disperse absorbed heat evenly. Instead of trapping it, they release thermal energy gradually, reducing stress on both the film and the paint surface below.
The Relationship Between Gloss, Clarity, and Heat Exposure
Why Some Films Turn Hazy or Discolored Under Intense Sun
When lower-grade PPF is overexposed to heat, its top coat can oxidize, leading to a cloudy or matte appearance. This change doesn’t just affect looks—it reduces UV efficiency and surface smoothness. Premium films remain optically stable even under constant heat.
The Role of Anti-Yellowing Additives in Long-Term Clarity
Anti-yellowing additives protect against polymer oxidation. They convert UV energy into harmless thermal energy, preventing the chemical reactions that cause discoloration. As a result, the film remains virtually invisible on the car’s surface for years.
Self-Healing and Thermal Activation Explained
How Warmth Restores Surface Smoothness
The top coat of paint protection film contains elastic polymers with memory. When scratched, these polymers rearrange when exposed to mild heat—like sunlight or warm water. The surface gradually returns to its smooth, original state, erasing light scuffs naturally.
The Limits of Self-Healing in Prolonged Heat Conditions
While heat activates healing, extreme or constant exposure can push polymers beyond their designed elasticity. Continuous heat above recommended thresholds may cause over-softening, which is why balanced thermal resistance is crucial in premium films.
Long-Term Effects of Continuous Sunlight Exposure
Structural Fatigue and Polymer Aging
Over the years, repeated heating and cooling cycles can cause structural fatigue. This leads to reduced flexibility and minor stiffness in the polymer. However, films designed for long-term use include stabilizers that slow down this natural aging process significantly.
Maintaining Optical Stability in Harsh Climates
Films that maintain transparency under sun exposure rely on cross-linked polymers. These molecular bonds ensure that clarity remains high, even after years in sunny environments, protecting both paint quality and visual appeal.
How Paint Protection Film Adapts to Different Environments
Behavior in Desert vs. Humid Conditions
In dry, hot regions, PPF faces intense heat and UV exposure. Its thermoplastic core manages expansion to prevent cracking. In humid climates, moisture resistance ensures no clouding or delamination occurs beneath the surface.
Adaptability in Urban Heat Zones
Urban areas with reflective surfaces and high ambient temperatures challenge surface coatings. Paint protection film in these environments resists heat buildup through reflective layers that disperse infrared radiation, keeping surface temperature stable.
Testing and Scientific Evaluation
Accelerated Weathering and Lab Simulation Methods
Laboratories test PPF by simulating years of UV and thermal exposure using xenon arc lamps and humidity chambers. These accelerated aging tests measure gloss retention, tensile strength, and clarity over extended periods.
What Real-World Field Testing Reveals
Vehicles in climates like Arizona and Florida often serve as real-world case studies. Results show that high-grade PPF retains over 90% of its optical and mechanical properties even after years of extreme sun exposure.
The Evolution of Heat-Resistant PPF Technology
Nano ceramic Additives and Advanced Material Science
Nano ceramic particles are now infused within the film to reflect infrared rays and reduce surface heat absorption. These innovations enhance the durability and UV resistance of modern paint protection film, pushing the boundaries of material engineering.
Future Innovations in Thermal-Responsive Films
Researchers are developing intelligent polymers that adapt their flexibility based on surrounding temperatures. These smart films could automatically adjust thermal resistance, ensuring consistent performance in every climate.
TintedAF Serving the Warrendale Community and Beyond in Detroit, MI
TintedAF is dedicated to serving the diverse needs of the local community of Detroit, MI, including individuals residing in neighborhood like Warrendale Community. With its convenient location near landmarks such as the “Masjid Tawheed, Simanek Park” and major intersections like Ford Rd (MI-153) & Mercury Dr and Hubbard Dr & Evergreen Rd (coordinates: 42.33189310, -83.21190720) we offer Paint Protection Film services.
Get Paint Protection Film Services at Warrendale Community Now
Navigate from Warrendale Community to TintedAF Now
What Happens to Paint Protection Film Under Extreme Heat and Sun Exposure?
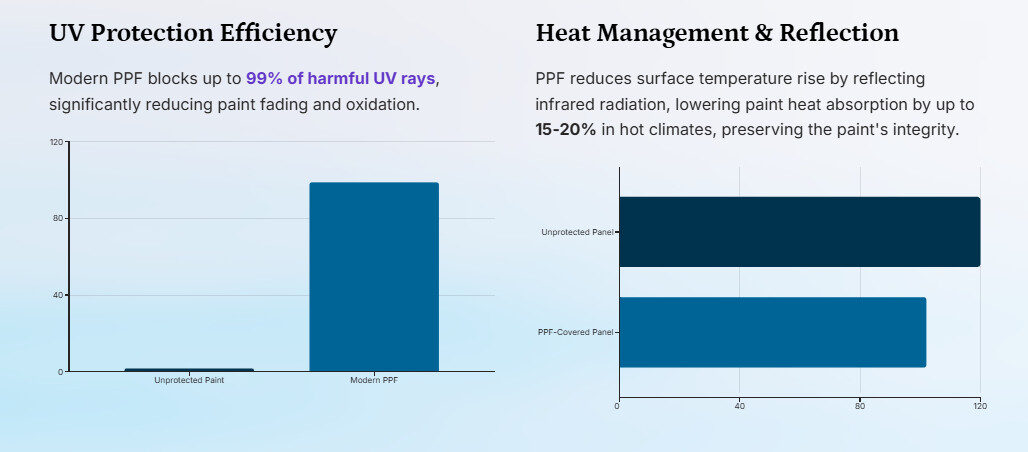
- UV Protection Efficiency:
- Modern PPF blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays, significantly reducing paint fading and oxidation (CCADetailing, 2025).
- UV transmission reduction graph: 0% (no film) → 99% (modern PPF).
- Heat Management:
- PPF reduces surface temperature rise by reflecting infrared radiation, lowering paint heat absorption by up to 15-20% in hot climates (CM3Detail, 2024).
- Chart: Surface temperature comparison (Unprotected vs. PPF-covered panels under 100°F ambient).
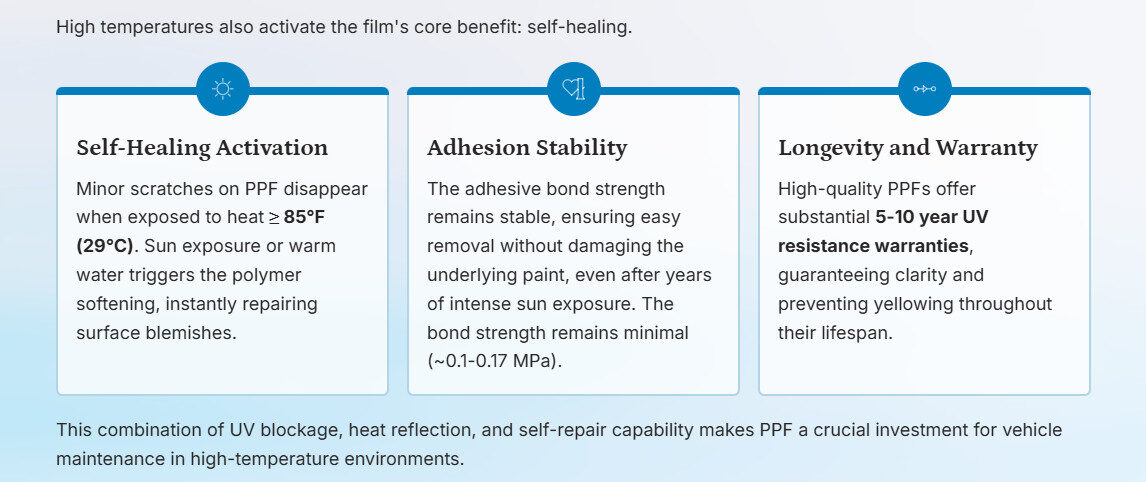
- Self-Healing Properties Activated by Heat:
- Minor scratches on PPF disappear when exposed to heat ≥ 85°F (29°C), using sun or warm water to trigger polymer softening (3M FAQ, 2023).
- Visual: Scratch depth before and after heat exposure.
- Durability & Adhesion Under Heat:
- Adhesive bond strength remains stable after years of sun exposure, increasing slightly from 0.075 MPa to 0.17 MPa, ensuring easy removal without paint damage (Detail Authority, 2024).
- Bar graph: Adhesive bond strength vs. paint bond strength (paint 16-25 MPa vs. PPF adhesive ~0.1-0.17 MPa).
- Longevity & Warranty:
- High-quality PPFs offer 5-10 years UV resistance warranties, maintaining clarity and preventing yellowing in extreme sun (LMCarDetailing, 2025).
- Timeline chart: Color retention over 10 years with PPF vs. without.
- Additional Benefits:
- Combined with ceramic coatings, PPF enhances gloss retention and further heat protection.
- Vehicles with PPF have up to 50% fewer paint-related complaints over 5 years and can sell for 15% higher resale value (GarvinAuto, 2025).
Visual elements:
- UV blocking efficiency line graph
- Temperature reduction bar chart
- Before/after scratch healing images
- Adhesive strength comparison bar chart
- Longevity timeline with warranty overlay


Sources: CCADetailing (2025), CM3Detail (2024), 3M FAQ (2023), Detail Authority (2024), LMCarDetailing (2025), GarvinAuto (2025)
Extreme heat and sunlight are two of the toughest challenges for any vehicle finish. Paint protection film acts as a shield, preserving color, gloss, and integrity against molecular breakdown caused by UV and infrared radiation.
At TINTEDAF, understanding how PPF reacts under these conditions allows us to appreciate the complex science behind its performance. It’s a remarkable example of how chemistry, engineering, and innovation work together to protect modern automotive finishes from the harshest elements.
FAQs
Does paint protection film melt under extreme heat?
No. High-quality films are engineered to tolerate surface temperatures well beyond typical driving conditions without melting or deforming.
How does sunlight affect the clarity of paint protection film?
Prolonged sunlight can cause oxidation in low-quality films, but stabilized materials resist yellowing and maintain transparency.
Can paint protection film lose adhesion from constant heat?
Only poor adhesives are affected. Premium PPFs maintain bond strength even after long-term exposure to high temperatures.
Does PPF stop UV damage completely?
It blocks most UV rays and significantly reduces oxidation, but ongoing maintenance helps extend its protective benefits.
How do modern films stay flexible in hot weather?
Thermoplastic polymers expand with heat and contract when cooled, maintaining elasticity without cracking or peeling.

